310386: CF1825E. LuoTianyi and XOR-Tree
Description
LuoTianyi gives you a tree with values in its vertices, and the root of the tree is vertex $1$.
In one operation, you can change the value in one vertex to any non-negative integer.
Now you need to find the minimum number of operations you need to perform to make each path from the root to leaf$^{\dagger}$ has a bitwise XOR value of zero.
$^{\dagger}$A leaf in a rooted tree is a vertex that has exactly one neighbor and is not a root.
InputThe first line contains a single integer $n$ ($2 \le n \le 10^5$) — the number of vertices in the tree.
The second line contains $n$ integers $a_1, a_2, \ldots, a_n$ ($1 \le a_i \le 10^9$), the $i$-th number represents the value in the $i$-th vertex.
Next $n−1$ lines describe the edges of the tree. The $i$-th line contains two integers $u_i$ and $v_i$ ($1 \le u_i,v_i \le n, u_i \neq v_i$) — the vertices connected by an edge of the tree. It's guaranteed that the given edges form a tree.
OutputPrint a single integer — the minimum number of operations.
ExamplesInput6 3 5 7 5 8 4 1 2 1 3 1 4 3 5 4 6Output
3Input
8 7 10 7 16 19 9 16 11 1 5 4 2 6 5 5 2 7 2 2 3 3 8Output
3Input
4 1 2 1 2 1 2 2 3 4 3Output
0Input
9 4 3 6 1 5 5 5 2 7 1 2 2 3 4 1 4 5 4 6 4 7 8 1 8 9Output
2Note
The tree in the first example:
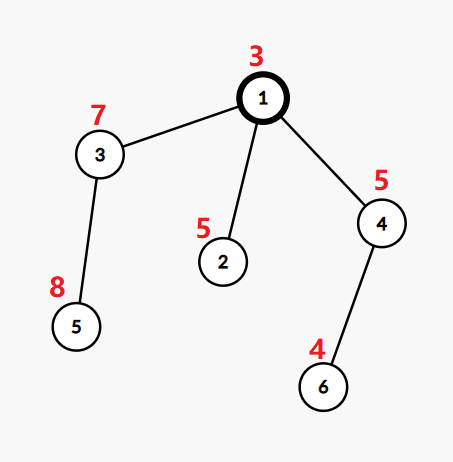
If we change the value in the vertex $2$ to $3$, the value in the vertex $5$ to $4$, and the value in the vertex $6$ to $6$, then the tree will be ok.
The bitwise XOR from the root to the leaf $2$ will be $3 \oplus 3=0$.
The bitwise XOR from the root to the leaf $5$ will be $4 \oplus 7 \oplus 3=0$.
The bitwise XOR from the root to the leaf $6$ will be $6 \oplus 5 \oplus 3=0$.
The tree in the second example:
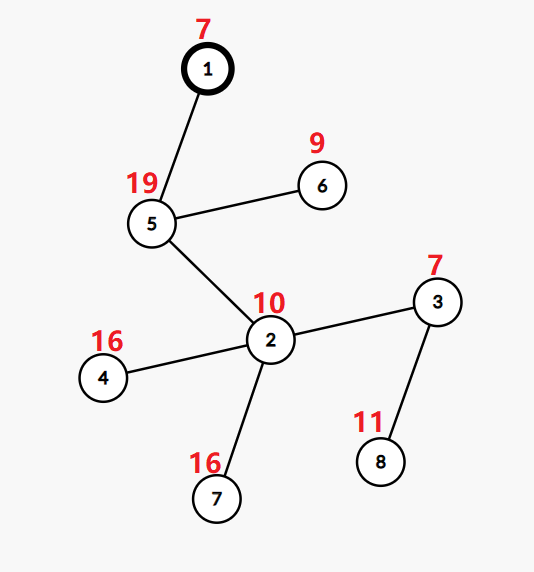
If we change the value in the vertex $2$ to $4$, the value in the vertex $3$ to $27$, and the value in the vertex $6$ to $20$, then the tree will be ok.
The bitwise XOR from the root to the leaf $6$ will be $20 \oplus 19 \oplus 7=0$.
The bitwise XOR from the root to the leaf $8$ will be $11 \oplus 27 \oplus 4 \oplus 19 \oplus 7=0$.
The bitwise XOR from the root to the leaf $4$ will be $16 \oplus 4 \oplus 19 \oplus 7=0$.
The bitwise XOR from the root to the leaf $7$ will be $16 \oplus 4 \oplus 19 \oplus 7=0$.
In the third example, the only leaf is the vertex $4$ and the bitwise XOR on the path to it is $1 \oplus 2 \oplus 1 \oplus 2 = 0$, so we don't need to change values.
In the fourth example, we can change the value in the vertex $1$ to $5$, and the value in the vertex $4$ to $0$.
Here $\oplus$ denotes the bitwise XOR operation.
Input
Output
输入数据格式:
- 第一行一个整数n(2≤n≤10^5),表示顶点的数量。
- 第二行n个整数a_1, a_2, ..., a_n(1≤a_i≤10^9),分别表示每个顶点的值。
- 接下来n-1行,每行两个整数u_i和v_i(1≤u_i,v_i≤n, u_i≠v_i),表示树中的一条边。
输出数据格式:
- 输出一个整数,表示所需的最少操作次数。
示例输入输出已给出,具体见题目描述。
公式使用LaTeX格式表示,例如按位异或操作表示为 $ a \oplus b $。题目大意:给定一个以1号顶点为根的树,每个顶点有一个值。可以通过一次操作将某个顶点的值改变为任何非负整数。要求通过最少的操作次数,使得从根到每个叶子节点的路径上的按位异或(XOR)值为零。 输入数据格式: - 第一行一个整数n(2≤n≤10^5),表示顶点的数量。 - 第二行n个整数a_1, a_2, ..., a_n(1≤a_i≤10^9),分别表示每个顶点的值。 - 接下来n-1行,每行两个整数u_i和v_i(1≤u_i,v_i≤n, u_i≠v_i),表示树中的一条边。 输出数据格式: - 输出一个整数,表示所需的最少操作次数。 示例输入输出已给出,具体见题目描述。 公式使用LaTeX格式表示,例如按位异或操作表示为 $ a \oplus b $。