310376: CF1824B1. LuoTianyi and the Floating Islands (Easy Version)
Description
This is the easy version of the problem. The only difference is that in this version $k\le\min(n,3)$. You can make hacks only if both versions of the problem are solved.
 Chtholly and the floating islands.
Chtholly and the floating islands. LuoTianyi now lives in a world with $n$ floating islands. The floating islands are connected by $n-1$ undirected air routes, and any two of them can reach each other by passing the routes. That means, the $n$ floating islands form a tree.
One day, LuoTianyi wants to meet her friends: Chtholly, Nephren, William, .... Totally, she wants to meet $k$ people. She doesn't know the exact positions of them, but she knows that they are in pairwise distinct islands. She define an island is good if and only if the sum of the distances$^{\dagger}$ from it to the islands with $k$ people is the minimal among all the $n$ islands.
Now, LuoTianyi wants to know that, if the $k$ people are randomly set in $k$ distinct of the $n$ islands, then what is the expect number of the good islands? You just need to tell her the expect number modulo $10^9+7$.
$^{\dagger}$The distance between two islands is the minimum number of air routes you need to take to get from one island to the other.
InputThe first line contains two integers $n$ and $k$ ($1\le k \le \min(n,3), 1\le n \le 2\cdot 10^5$) — the number of the islands and people respectively.
Next $n−1$ lines describe the air routes. The $i$-th of them contains two integers $u_i$ and $v_i$ ($1 \le u_i,v_i \le n, u_i \neq v_i$) — the islands connected by the $i$-th air route.
OutputPrint a single integer — the expect number of the good islands modulo $10^9 + 7$.
Formally, let $M = 10^9 + 7$. It can be shown that the answer can be expressed as an irreducible fraction $\frac{p}{q}$, where $p$ and $q$ are integers and $q \not \equiv 0$ ($\operatorname{mod} M$). Output the integer equal to $p \cdot q^{-1}$ $\operatorname{mod} M$. In other words, output such an integer $x$ that $0 \le x < M$ and $x \cdot q \equiv p$ ($\operatorname{mod} M$).
ExamplesInput4 2 1 2 2 3 3 4Output
666666674Input
5 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 3 5Output
1Note
In the first example the air routes form the following tree:
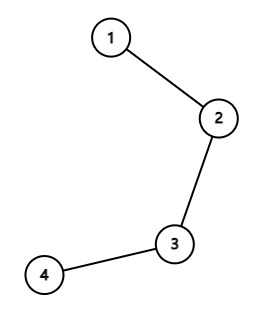
If the people are in the islands $1$ and $2$, then islands $1$ and $2$ will be good.
The sum of the distances from island $1$ or $2$ to all the people is $1+0=1$, which is the minimal. While the sum of the distances from island $3$ to all the people is $2+1=3$, which is greater than $1$.
Like this, when the people are in island $1$ and $3$, then islands $1,2$ and $3$ will be good.
When the people are in islands $1$ and $4$, then islands $1,2,3$ and $4$ will be good.
When the people are in islands $2$ and $3$, then islands $2$ and $3$ will be good.
When the people are in islands $2$ and $4$, then islands $2,3$ and $4$ will be good.
When the people are in islands $3$ and $4$, then islands $3$ and $4$ will be good.
So the expect of the number of the good islands is $\frac{16}{6}$, which equals to $666666674$ modulo $10^9+7$.
In the second example the air routes form the following tree:
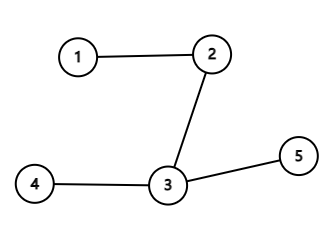
There is always the only good island, so the expected number is $1$.
Input
题意翻译
给定一棵 $n$ 个结点的树,现在有 $k(k\le \min(n,3))$ 个结点上有人。 一个结点是好的当且仅当这个点到所有人的距离之和最小。 求在这 $n$ 个点中随机取 $k$ 个点时,好的结点的期望个数,对 $10^9+7$ 取模。Output
题目大意:
洛天依生活在一个有 n 个浮动岛屿的世界里。这些岛屿通过 n-1 条无向航线相连,任何两个岛屿都可以通过这些航线相互到达,形成了一棵树。有一天,洛天依想见她的朋友们:克托莉、涅弗伦、威廉……总共她想见 k 个人。她不知道他们确切的位置,但知道他们分别位于 k 个不同的岛屿上。定义一个岛屿是“好的”,当且仅当它到这 k 个岛屿的距离之和在所有 n 个岛屿中最小。现在,洛天依想知道,如果这 k 个人随机分布在 n 个岛屿中的 k 个不同的岛屿上,那么“好的岛屿”的期望数量是多少?需要输出这个期望数量模 10^9+7 的结果。
输入数据格式:
第一行包含两个整数 n 和 k(1≤k≤min(n,3), 1≤n≤2×10^5)——岛屿的数量和人数。
接下来 n-1 行描述航线。第 i 行包含两个整数 u_i 和 v_i(1≤u_i,v_i≤n, u_i≠v_i)——第 i 条航线连接的两个岛屿。
输出数据格式:
输出一个整数——好的岛屿的期望数量模 10^9+7 的结果。
正式地说,设 M=10^9+7。答案可以表示为一个不可约分数 p/q,其中 p 和 q 是整数,且 q 不等于 0(mod M)。输出等于 p⋅q^(-1) mod M 的整数。换句话说,输出一个整数 x,使得 0≤x
示例:
输入:
4 2
1 2
2 3
3 4
输出:
666666674
输入:
5 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
3 5
输出:
1
注意:
在第一个示例中,如果人们在岛屿 1 和 2 上,那么岛屿 1 和 2 将是好的。从岛屿 1 或 2 到所有人的距离之和是 1+0=1,这是最小的。而从岛屿 3 到所有人的距离之和是 2+1=3,大于 1。以此类推,当人们在岛屿 1 和 3 上时,岛屿 1、2 和 3 将是好的;当人们在岛屿 1 和 4 上时,岛屿 1、2、3 和 4 将是好的;当人们在岛屿 2 和 3 上时,岛屿 2 和 3 将是好的;当人们在岛屿 2 和 4 上时,岛屿 2、3 和 4 将是好的;当人们在岛屿 3 和 4 上时,岛屿 3 和 4 将是好的。所以好的岛屿的期望数量是 16/6,等于 666666674 模 10^9+7。
在第二个示例中,总是只有一个好的岛屿,所以期望数量是 1。洛天依和浮动岛屿(简单版本) 题目大意: 洛天依生活在一个有 n 个浮动岛屿的世界里。这些岛屿通过 n-1 条无向航线相连,任何两个岛屿都可以通过这些航线相互到达,形成了一棵树。有一天,洛天依想见她的朋友们:克托莉、涅弗伦、威廉……总共她想见 k 个人。她不知道他们确切的位置,但知道他们分别位于 k 个不同的岛屿上。定义一个岛屿是“好的”,当且仅当它到这 k 个岛屿的距离之和在所有 n 个岛屿中最小。现在,洛天依想知道,如果这 k 个人随机分布在 n 个岛屿中的 k 个不同的岛屿上,那么“好的岛屿”的期望数量是多少?需要输出这个期望数量模 10^9+7 的结果。 输入数据格式: 第一行包含两个整数 n 和 k(1≤k≤min(n,3), 1≤n≤2×10^5)——岛屿的数量和人数。 接下来 n-1 行描述航线。第 i 行包含两个整数 u_i 和 v_i(1≤u_i,v_i≤n, u_i≠v_i)——第 i 条航线连接的两个岛屿。 输出数据格式: 输出一个整数——好的岛屿的期望数量模 10^9+7 的结果。 正式地说,设 M=10^9+7。答案可以表示为一个不可约分数 p/q,其中 p 和 q 是整数,且 q 不等于 0(mod M)。输出等于 p⋅q^(-1) mod M 的整数。换句话说,输出一个整数 x,使得 0≤x