311119: CF1937B. Binary Path
Description
You are given a $2 \times n$ grid filled with zeros and ones. Let the number at the intersection of the $i$-th row and the $j$-th column be $a_{ij}$.
There is a grasshopper at the top-left cell $(1, 1)$ that can only jump one cell right or downwards. It wants to reach the bottom-right cell $(2, n)$. Consider the binary string of length $n+1$ consisting of numbers written in cells of the path without changing their order.
Your goal is to:
- Find the lexicographically smallest$^\dagger$ string you can attain by choosing any available path;
- Find the number of paths that yield this lexicographically smallest string.
$^\dagger$ If two strings $s$ and $t$ have the same length, then $s$ is lexicographically smaller than $t$ if and only if in the first position where $s$ and $t$ differ, the string $s$ has a smaller element than the corresponding element in $t$.
InputEach test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains the number of test cases $t$ ($1 \le t \le 10^4$). The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer $n$ ($2 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5$).
The second line of each test case contains a binary string $a_{11} a_{12} \ldots a_{1n}$ ($a_{1i}$ is either $0$ or $1$).
The third line of each test case contains a binary string $a_{21} a_{22} \ldots a_{2n}$ ($a_{2i}$ is either $0$ or $1$).
It is guaranteed that the sum of $n$ over all test cases does not exceed $2 \cdot 10^5$.
OutputFor each test case, output two lines:
- The lexicographically smallest string you can attain by choosing any available path;
- The number of paths that yield this string.
3 2 00 00 4 1101 1100 8 00100111 11101101Output
000 2 11000 1 001001101 4Note
In the first test case, the lexicographically smallest string is $\mathtt{000}$. There are two paths that yield this string:
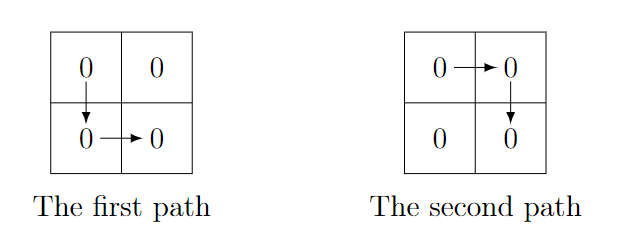
In the second test case, the lexicographically smallest string is $\mathtt{11000}$. There is only one path that yields this string:
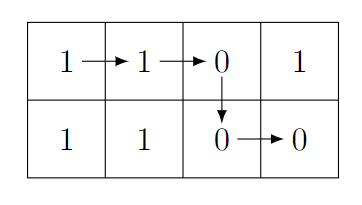
Output
1. 通过选择任意可用的路径,可以得到字典序最小的字符串。
2. 产生这个字典序最小字符串的路径数量。
输入数据格式:第一行包含测试用例的数量t(1≤t≤10^4)。接下来每个测试用例包含三行,第一行是一个整数n(2≤n≤2×10^5),表示网格的宽度。第二行和第三行各包含一个长度为n的二进制字符串,表示网格的第一行和第二行的数值。
输出数据格式:对于每个测试用例,输出两行,第一行是字典序最小的字符串,第二行是产生这个字符串的路径数量。题目大意:给定一个2×n的网格,网格中填充了0和1。一个蚂蚱从左上角(1,1)出发,只能向右或向下跳,要到达右下角(2,n)。求: 1. 通过选择任意可用的路径,可以得到字典序最小的字符串。 2. 产生这个字典序最小字符串的路径数量。 输入数据格式:第一行包含测试用例的数量t(1≤t≤10^4)。接下来每个测试用例包含三行,第一行是一个整数n(2≤n≤2×10^5),表示网格的宽度。第二行和第三行各包含一个长度为n的二进制字符串,表示网格的第一行和第二行的数值。 输出数据格式:对于每个测试用例,输出两行,第一行是字典序最小的字符串,第二行是产生这个字符串的路径数量。