311004: CF1919H. Tree Diameter
Description
There is a hidden tree with $n$ vertices. The $n-1$ edges of the tree are numbered from $1$ to $n-1$. You can ask the following queries of two types:
- Give the grader an array $a$ with $n - 1$ positive integers. For each edge from $1$ to $n - 1$, the weight of edge $i$ is set to $a_i$. Then, the grader will return the length of the diameter$^\dagger$.
- Give the grader two indices $1 \le a, b \le n - 1$. The grader will return the number of edges between edges $a$ and $b$. In other words, if edge $a$ connects $u_a$ and $v_a$ while edge $b$ connects $u_b$ and $v_b$, the grader will return $\min(\text{dist}(u_a, u_b), \text{dist}(v_a, u_b), \text{dist}(u_a, v_b), \text{dist}(v_a, v_b))$, where $\text{dist}(u, v)$ represents the number of edges on the path between vertices $u$ and $v$.
Find any tree isomorphic$^\ddagger$ to the hidden tree after at most $n$ queries of type 1 and $n$ queries of type 2 in any order.
$^\dagger$ The distance between two vertices is the sum of the weights on the unique simple path that connects them. The diameter is the largest of all those distances.
$^\ddagger$ Two trees, consisting of $n$ vertices each, are called isomorphic if there exists a permutation $p$ containing integers from $1$ to $n$ such that edge ($u$, $v$) is present in the first tree if and only if the edge ($p_u$, $p_v$) is present in the second tree.
InputThe first and only line of input contains a single integer $n$ ($3 \le n \le 1000$) — the number of vertices in the tree.
InteractionBegin the interaction by reading $n$.
You are allowed to make queries in the following way:
- "$\mathtt{?}\,1\,a_1\,a_2 \ldots a_{n-1}$" ($1 \le a_i \le 10^9$). Then, you should read an integer $k$ which represents the length of the diameter. You are only allowed to ask this query at most $n$ times.
- "$\mathtt{?}\,2\,a\,b$" ($1 \le a, b \le n - 1$). Then, you should read an integer $k$ which represents the number of edges between edges $a$ and $b$. You are only allowed to ask this query at most $n$ times.
In case your query is invalid. the program will terminate immediately and you will receive Wrong answer verdict.
To give the final answer, print "!" on a single line, followed by $n - 1$ lines where line $i$ contains "$u_i\,v_i$" ($1 \le u_i, v_i \le n$) which represents that for each $i$ from $1$ to $n-1$, there is an edge between $u_i$ and $v_i$.
After printing a query do not forget to output end of line and flush the output. Otherwise, you will get Idleness limit exceeded. To do this, use:
- fflush(stdout) or cout.flush() in C++;
- System.out.flush() in Java;
- flush(output) in Pascal;
- stdout.flush() in Python;
- see documentation for other languages.
Hacks
The first line contains a single integer $n$ ($3 \le n \le 1000$) — the number of vertices in the tree.
The next $n - 1$ lines contain two integers each $u_i, v_i$ ($1 \le u_i, v_i \le n$) — the edges of the tree.
ExampleInput5 3 1 9 0Output
? 1 1 1 1 1 ? 2 1 3 ? 1 4 3 2 1 ? 2 4 2 ! 3 1 4 2 1 2 2 5Note
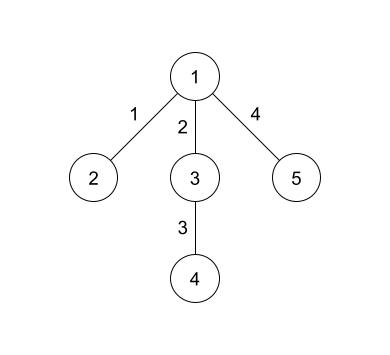
The hidden tree in the example is shown above. The number on the vertices represents the vertex number while the number on the edges represents the edge number.
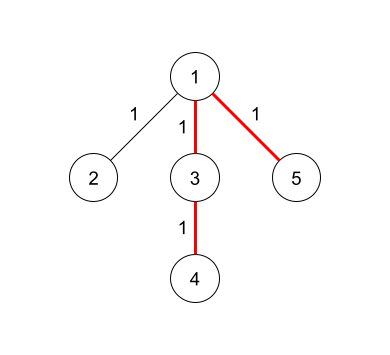
In the first query, all the edges are set to weight $1$, so the diameter has length $3$ as shown in the diagram.
In the second query, there is $1$ edge between edges $1$ and $3$.
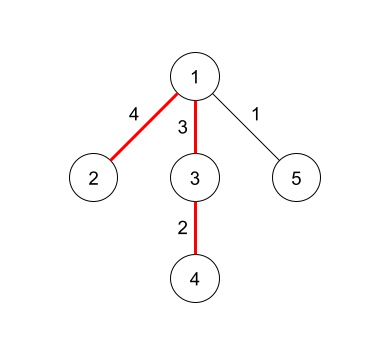
In the third query, the diameter is $9$ by taking edges $1$, $2$ and $3$.
In the fourth query, there are no edges between edges $4$ and $2$.
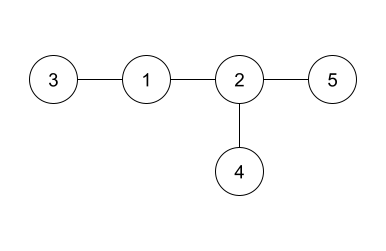
The answer given in the example is shown in the above diagram. Since it is isomorphic to the hidden tree, it is accepted as a correct answer. Note that the edges can be printed in any order.
Output
1. 提供一个数组a,包含n-1个正整数。对于每条边i,设置边i的权重为a_i。然后,程序将返回直径的长度。
2. 提供两个索引a和b。程序将返回边a和边b之间的边数。换句话说,如果边a连接u_a和v_a,边b连接u_b和v_b,则程序将返回min(dist(u_a, u_b), dist(v_a, u_b), dist(u_a, v_b), dist(v_a, v_b)),其中dist(u, v)表示顶点u和v之间路径上的边数。
在最多n次类型1查询和n次类型2查询的任意顺序下,找到隐藏树的同构树。
输入输出数据格式:
输入:
- 第一行包含一个整数n(3≤n≤1000),表示树中的顶点数。
交互:
- 可以通过以下方式提出查询:
1. "? 1 a_1 a_2 ... a_{n-1}" (1≤a_i≤10^9)。然后,读取一个整数k,表示直径的长度。最多允许进行n次此查询。
2. "? 2 a b" (1≤a, b≤n-1)。然后,读取一个整数k,表示边a和边b之间的边数。最多允许进行n次此查询。
- 如果查询无效,程序将立即终止,并收到"Wrong answer"的判断。
- 要给出最终答案,在一行打印"!",然后是n-1行,每行包含"u_i v_i"(1≤u_i, v_i≤n),表示对于每个i从1到n-1,存在一条边连接u_i和v_i。
示例:
输入:
```
5
```
输出:
```
? 1 1 1 1 1
? 2 1 3
? 1 4 3 2 1
? 2 4 2
!
3 1
4 2
1 2
2 5
```
注意:隐藏树在示例中如上图所示。顶点上的数字表示顶点编号,边上的数字表示边编号。题目大意:在给定的隐树中,有n个顶点和n-1条边,编号从1到n-1。可以通过两种类型的查询来找到这个树的同构树: 1. 提供一个数组a,包含n-1个正整数。对于每条边i,设置边i的权重为a_i。然后,程序将返回直径的长度。 2. 提供两个索引a和b。程序将返回边a和边b之间的边数。换句话说,如果边a连接u_a和v_a,边b连接u_b和v_b,则程序将返回min(dist(u_a, u_b), dist(v_a, u_b), dist(u_a, v_b), dist(v_a, v_b)),其中dist(u, v)表示顶点u和v之间路径上的边数。 在最多n次类型1查询和n次类型2查询的任意顺序下,找到隐藏树的同构树。 输入输出数据格式: 输入: - 第一行包含一个整数n(3≤n≤1000),表示树中的顶点数。 交互: - 可以通过以下方式提出查询: 1. "? 1 a_1 a_2 ... a_{n-1}" (1≤a_i≤10^9)。然后,读取一个整数k,表示直径的长度。最多允许进行n次此查询。 2. "? 2 a b" (1≤a, b≤n-1)。然后,读取一个整数k,表示边a和边b之间的边数。最多允许进行n次此查询。 - 如果查询无效,程序将立即终止,并收到"Wrong answer"的判断。 - 要给出最终答案,在一行打印"!",然后是n-1行,每行包含"u_i v_i"(1≤u_i, v_i≤n),表示对于每个i从1到n-1,存在一条边连接u_i和v_i。 示例: 输入: ``` 5 ``` 输出: ``` ? 1 1 1 1 1 ? 2 1 3 ? 1 4 3 2 1 ? 2 4 2 ! 3 1 4 2 1 2 2 5 ``` 注意:隐藏树在示例中如上图所示。顶点上的数字表示顶点编号,边上的数字表示边编号。