310333: CF1819C. The Fox and the Complete Tree Traversal
Description
The fox Yae climbed the tree of the Sacred Sakura. A tree is a connected undirected graph that does not contain cycles.
The fox uses her magical powers to move around the tree. Yae can jump from vertex $v$ to another vertex $u$ if and only if the distance between these vertices does not exceed $2$. In other words, in one jump Yae can jump from vertex $v$ to vertex $u$ if vertices $v$ and $u$ are connected by an edge, or if there exists such vertex $w$ that vertices $v$ and $w$ are connected by an edge, and also vertices $u$ and $w$ are connected by an edge.
After Yae was able to get the sakura petal, she wondered if there was a cyclic route in the tree $v_1, v_2, \ldots, v_n$ such that:
- the fox can jump from vertex $v_i$ to vertex $v_{i + 1}$,
- the fox can jump from vertex $v_n$ to vertex $v_1$,
- all $v_i$ are pairwise distinct.
Help the fox determine if the required traversal exists.
InputThe first line contains one integer $n$ ($2 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5$) —the number of vertices of the tree.
Each of the following $n - 1$ lines contains two integers $u$ and $v$ ($1 \le u, v \le n$, $u \ne v$) — vertices connected by an edge. It is guaranteed that these edges form a tree.
OutputOn the first line, print "Yes" (without quotes) if the required route of the tree exists, or "No" (without quotes) otherwise.
If the required tree traversal exists, on the second line print $n$ integers of different integers $v_1, v_2, \ldots, v_n$ ($1 \le v_i \le n$) — the vertices of the tree in traversal order.
If there are several correct traversals, output any of them.
ExamplesInput5 1 2 1 3 3 4 3 5Output
Yes 4 5 1 2 3Input
3 1 2 1 3Output
Yes 1 2 3Input
15 1 2 1 3 2 4 2 5 3 6 3 7 4 8 4 9 5 10 5 11 6 12 6 13 7 14 7 15Output
NoNote
The tree from the first example is shown below. The bold arrows indicate the fox's route.
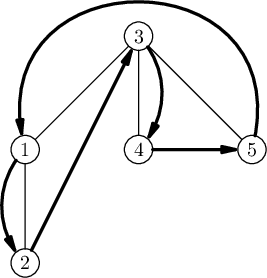
In the second example, any sequence of three different vertices is a correct route, because the fox can jump from any vertex to any vertex.
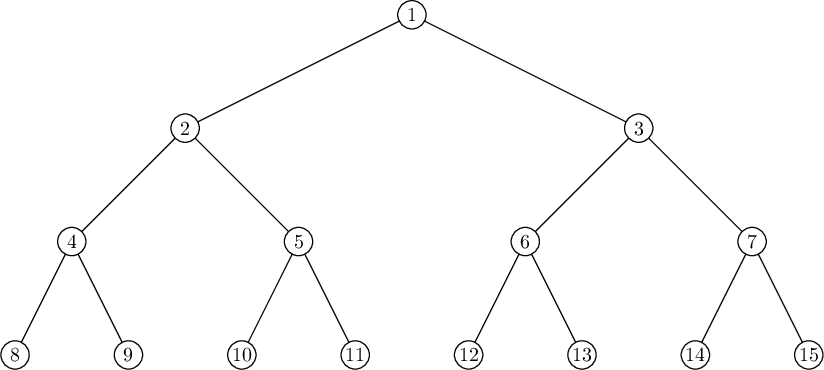
The tree from the third example is shown below. It can be shown that there is no required route for it.
Input
题意翻译
### 题目描述 给定整数 $n$ 和一棵包含 $n$ 个节点的树。 记 $\text{Dist}(x,y)$ 表示树上节点 $x,y$ 之间最短路径的边数。 你需要判断是否存在一个 $1\sim n$ 的排列 $p$,满足: - $\text{Dist}(p_i,p_{i+1})\leq 2$ 对任意整数 $i(1\leq i<n)$ 成立。 - $\text{Dist}(p_1,p_n)\leq2$。 存在则输出 `Yes` 然后输出任意一个满足要求的 $p$,不存在则输出 `No`。 ### 输入格式 第一行输入一个整数 $n(2\leq n\leq2\times10^5)$。 接下来输入 $n-1$ 行,每行输入两个整数 $u,v(1\leq u,v\leq n;u\not=v)$,表示树的节点 $u,v$ 之间有一条边。 保证给定的是棵树。 ### 输出格式 对于每组数据: 如果不存在满足要求的 $p$,输出一行 `No`。 否则: - 首先输出一行 `Yes`。 - 接下来输出一行 $n$ 个整数表示你所构造的满足要求的排列 $p$。 如果有多个满足要求的 $p$,输出任意一个即可。 ### 样例解释 下方的图片分别展示了样例一和样例三对应的树。Output
题目描述了一个狐狸在樱花树上跳跃的问题。狐狸可以从一个节点跳到另一个节点,条件是这两个节点之间的距离不超过2,也就是说,狐狸可以跳到直接相连的节点,或者通过一个中间节点跳到一个与之相连的节点。题目要求判断是否存在一个循环的路径,满足狐狸可以从一个节点跳到下一个节点,并且最后一个节点可以跳回到第一个节点,且路径上的所有节点都是不同的。
**输入数据格式:**
第一行包含一个整数$n$($2 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5$),表示树中的节点数。
接下来的$n-1$行,每行包含两个整数$u$和$v$($1 \le u, v \le n$,$u \ne v$),表示节点$u$和节点$v$之间有一条边。保证这些边构成一棵树。
**输出数据格式:**
如果存在这样的路径,第一行输出"Yes"(不包括引号)。
第二行输出$n$个整数$v_1, v_2, \ldots, v_n$,表示路径上的节点顺序。
如果不存在这样的路径,输出"No"(不包括引号)。
如果存在多条正确的路径,输出其中任意一条即可。
**公式(LaTeX格式):**
- 跳跃条件:如果节点$v$和$u$直接相连,或者存在一个节点$w$使得$v$和$w$、$u$和$w$都直接相连,则狐狸可以从$v$跳到$u$。
- 循环路径条件:存在一个路径$v_1, v_2, \ldots, v_n$,使得狐狸可以从$v_i$跳到$v_{i+1}$,从$v_n$跳回到$v_1$,且所有$v_i$都是不同的。
**示例:**
输入:
```
5
1 2
1 3
3 4
3 5
```
输出:
```
Yes
4 5 1 2 3
```
输入:
```
3
1 2
1 3
```
输出:
```
Yes
1 2 3
```
输入:
```
15
1 2
1 3
2 4
2 5
3 6
3 7
4 8
4 9
5 10
5 11
6 12
6 13
7 14
7 15
```
输出:
```
No
```**题目大意:** 题目描述了一个狐狸在樱花树上跳跃的问题。狐狸可以从一个节点跳到另一个节点,条件是这两个节点之间的距离不超过2,也就是说,狐狸可以跳到直接相连的节点,或者通过一个中间节点跳到一个与之相连的节点。题目要求判断是否存在一个循环的路径,满足狐狸可以从一个节点跳到下一个节点,并且最后一个节点可以跳回到第一个节点,且路径上的所有节点都是不同的。 **输入数据格式:** 第一行包含一个整数$n$($2 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5$),表示树中的节点数。 接下来的$n-1$行,每行包含两个整数$u$和$v$($1 \le u, v \le n$,$u \ne v$),表示节点$u$和节点$v$之间有一条边。保证这些边构成一棵树。 **输出数据格式:** 如果存在这样的路径,第一行输出"Yes"(不包括引号)。 第二行输出$n$个整数$v_1, v_2, \ldots, v_n$,表示路径上的节点顺序。 如果不存在这样的路径,输出"No"(不包括引号)。 如果存在多条正确的路径,输出其中任意一条即可。 **公式(LaTeX格式):** - 跳跃条件:如果节点$v$和$u$直接相连,或者存在一个节点$w$使得$v$和$w$、$u$和$w$都直接相连,则狐狸可以从$v$跳到$u$。 - 循环路径条件:存在一个路径$v_1, v_2, \ldots, v_n$,使得狐狸可以从$v_i$跳到$v_{i+1}$,从$v_n$跳回到$v_1$,且所有$v_i$都是不同的。 **示例:** 输入: ``` 5 1 2 1 3 3 4 3 5 ``` 输出: ``` Yes 4 5 1 2 3 ``` 输入: ``` 3 1 2 1 3 ``` 输出: ``` Yes 1 2 3 ``` 输入: ``` 15 1 2 1 3 2 4 2 5 3 6 3 7 4 8 4 9 5 10 5 11 6 12 6 13 7 14 7 15 ``` 输出: ``` No ```