310325: CF1816A. Ian Visits Mary
Description
Ian and Mary are frogs living on lattice points of the Cartesian coordinate plane, with Ian living on $(0,0)$ and Mary living on $(a,b)$.
Ian would like to visit Mary by jumping around the Cartesian coordinate plane. Every second, he jumps from his current position $(x_p, y_p)$ to another lattice point $(x_q, y_q)$, such that no lattice point other than $(x_p, y_p)$ and $(x_q, y_q)$ lies on the segment between point $(x_p, y_p)$ and point $(x_q, y_q)$.
As Ian wants to meet Mary as soon as possible, he wants to jump towards point $(a,b)$ using at most $2$ jumps. Unfortunately, Ian is not good at maths. Can you help him?
A lattice point is defined as a point with both the $x$-coordinate and $y$-coordinate being integers.
InputThe first line contains a single integer $t$ ($1 \le t \le 500$) — the number of test cases. The description of test cases follows.
The first and only line of each test case contains two integers $a$ and $b$ ($1\le a,b\le 10^9$) — the coordinates of the lattice point where Mary lives.
OutputFor each test case, print an integer $n$ ($1 \le n \le 2$) on the first line, denoting the number of jumps Ian uses in order to meet Mary. Note that you do not need to minimize the number of jumps.
On the $i$-th line of the next $n$ lines, print two integers $0 \le x_i,y_i \le 10^9$ separated by a space, denoting Ian's location $(x_i,y_i)$ after the $i$-th jump. $x_n = a$, $y_n = b$ must hold.
Ian's initial location and his locations after each of the $n$ jumps need not be distinct.
If there are multiple solutions, output any.
ExampleInput8 3 4 4 4 3 6 2 2 1 1 7 3 2022 2023 1000000000 1000000000Output
1 3 4 2 3 2 4 4 2 5 3 3 6 2 1 0 2 2 1 1 1 1 7 3 1 2022 2023 2 69420420 469696969 1000000000 1000000000Note
In the first test case:
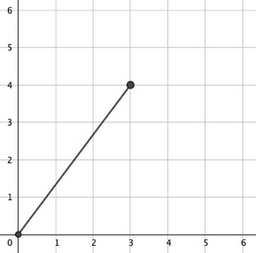
$(0,0) \to (3,4)$
In the second test case:
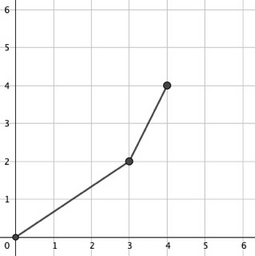
$(0,0) \to (3,2) \to (4,4)$
In the third test case:
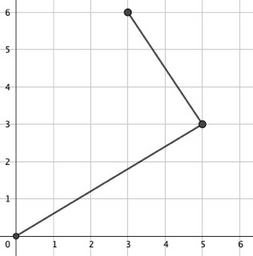
$(0,0) \to (5,3) \to (3,6)$
Input
题意翻译
### 题目描述 $\textrm{lan}$ 和 $\textrm{Mary}$ 是生活在笛卡尔坐标系格点上的青蛙,$\textrm{lan}$ 在 $(0,0)$,而 $\textrm{Mary}$ 在 $(a,b)$。 $\textrm{lan}$ 想在 笛卡尔坐标系上跳来跳去去访问 $\textrm{Mary}$。每一秒,他会从当前位置 $(x_p,y_p)$ 跳到整点 $(x_q,y_q)$,使得若用一条线段连接 $(x_p,y_p)$ 和 $(x_q,y_q)$,没有整点在这条线段上。 $\textrm{lan}$ 想尽快见到 $\textrm{Mary}$,所以他想用最多两次跳跃到 $(a,b)$。不幸的是,$\textrm{lan}$ 不太会数学,你能帮帮他吗? 整点被定义为 $x$ 坐标和 $y$ 坐标都是整数的点。 ### 输入格式 第一行包含一个整数 $t$ ( $1\le t\le 500$ ),表示测试数据的数量。 对于每一个数据: 只有一行包含两个正整数 $a,b$ ( $1\le a,b\le 10^9$ ),含义如题面所示。 ### 输出格式 对于每一个数据: 第一行是一个正整数 $n$ ( $1\le n\le 2$ ),表示 $\textrm{lan}$ 需要几次跳跃访问 $\textrm{Mary}$。**注意:你不需要让 $n$ 最小。** 下面是 $n$ 行,在第 $i$ 行有用空格分开的两个整数 $x_i,y_i$ ( $0\le x_i,y_i\le 10^9$ ),表示 $\textrm{lan}$ 第 $i$ 次会跳跃到 $(x_i,y_i)$。必须满足 $x_n=a,y_n=b$。 $\textrm{lan}$ 每次跳转后的位置不需要是不同的。 如果有多组解,输出任意一个。Output
Ian和Mary是生活在笛卡尔坐标系格点上的青蛙,Ian位于原点(0,0),Mary位于(a,b)。Ian希望通过跳跃访问Mary,每次跳跃必须到达另一个格点,并且跳跃路径上不能有其他格点。Ian希望使用最多两次跳跃尽快到达Mary的位置。需要帮助Ian找到跳跃的路径。
输入数据格式:
第一行包含一个整数t(1≤t≤500),表示测试用例的数量。接下来每个测试用例包含一行,有两个整数a和b(1≤a,b≤10^9),表示Mary所在的格点坐标。
输出数据格式:
对于每个测试用例,首先输出一个整数n(1≤n≤2),表示Ian到达Mary所需的跳跃次数。然后在接下来的n行中,每行输出两个整数x_i和y_i(0≤x_i,y_i≤10^9),表示Ian第i次跳跃后的位置。最后,Ian的位置必须满足x_n=a, y_n=b。如果有多个解决方案,输出任意一个即可。
请注意,Ian的初始位置以及每次跳跃后的位置可以不唯一。题目大意: Ian和Mary是生活在笛卡尔坐标系格点上的青蛙,Ian位于原点(0,0),Mary位于(a,b)。Ian希望通过跳跃访问Mary,每次跳跃必须到达另一个格点,并且跳跃路径上不能有其他格点。Ian希望使用最多两次跳跃尽快到达Mary的位置。需要帮助Ian找到跳跃的路径。 输入数据格式: 第一行包含一个整数t(1≤t≤500),表示测试用例的数量。接下来每个测试用例包含一行,有两个整数a和b(1≤a,b≤10^9),表示Mary所在的格点坐标。 输出数据格式: 对于每个测试用例,首先输出一个整数n(1≤n≤2),表示Ian到达Mary所需的跳跃次数。然后在接下来的n行中,每行输出两个整数x_i和y_i(0≤x_i,y_i≤10^9),表示Ian第i次跳跃后的位置。最后,Ian的位置必须满足x_n=a, y_n=b。如果有多个解决方案,输出任意一个即可。 请注意,Ian的初始位置以及每次跳跃后的位置可以不唯一。