310046: CF1775F. Laboratory on Pluto
Memory Limit:256 MB
Time Limit:2 S
Judge Style:Text Compare
Creator:
Submit:0
Solved:0
Description
Laboratory on Pluto
题目描述
As you know, Martian scientists are actively engaged in space research. One of the highest priorities is Pluto. In order to study this planet in more detail, it was decided to build a laboratory on Pluto. It is known that the lab will be built of $ n $ square blocks of equal size. For convenience, we will assume that Pluto's surface is a plane divided by vertical and horizontal lines into unit squares. Each square is either occupied by a lab block or not, and only $ n $ squares are occupied. Since each block is square, it has four walls. If a wall is adjacent to another block, it is considered inside, otherwise — outside. Pluto is famous for its extremely cold temperatures, so the outside walls of the lab must be insulated. One unit of insulation per exterior wall would be required. Thus, the greater the total length of the outside walls of the lab (i. e., its perimeter), the more insulation will be needed. Consider the lab layout in the figure below. It shows that the lab consists of $ n = 33 $ blocks, and all the blocks have a total of $ 24 $ outside walls, i. e. $ 24 $ units of insulation will be needed. You should build the lab optimally, i. e., minimize the amount of insulation. On the other hand, there may be many optimal options, so scientists may be interested in the number of ways to build the lab using the minimum amount of insulation, modulo a prime number $ m $ . Two ways are considered the same if they are the same when overlapping without turning. Thus, if a lab plan is rotated by $ 90^{\circ} $ , such a new plan can be considered a separate way. To help scientists explore Pluto, you need to write a program that solves these difficult problems. 输入输出格式
输入格式
The first line contains two integers $ t $ and $ u $ ( $ 1 \le t \le 2\cdot 10^5 $ , $ 1 \le u \le 2 $ ) — the number of test cases and the test type. If $ u=1 $ , you need to find any way to build the lab in an optimal way, and if $ u=2 $ , you need to calculate the number of ways to do it. If $ u=2 $ , then in the following line of input there is a prime integer $ m $ ( $ 10^8 \le m \le 10^9 + 9 $ ), modulo which you need to calculate the number of ways. Each of the following $ t $ lines of input contains a description of a test case consisting of one integer $ n $ ( $ 1 \le n \le 4\cdot 10^5 $ ) — the number of blocks the lab should consist of. It is guaranteed that if $ u=1 $ , then the sum of $ n $ on all test cases does not exceed $ 8\cdot10^5 $ .
输出格式
For each test case, output the answers in the format below, separating them with a newline. The output format depends on $ u $ in the input data. If $ u=1 $ , in the first line you need to print two integers $ h $ and $ w $ —the height and width of the area in which the lab should be built. Then, in each of the following $ h $ lines, you must output a line $ s_i $ consisting of $ w $ characters "\#" and ".". If the $ j $ -th character of the row $ s_i $ is "\#", then the corresponding square must contain a block of laboratory, otherwise, it is considered empty. Thus, we get a matrix of symbols. The condition must also be met that the first and last rows of the matrix, as well as the first and last columns, must have at least one character "\#", otherwise we could output the same lab layout, but with smaller $ h $ and $ w $ . If there are many options to build an optimal lab, you can print any of them. If $ u=2 $ , you need to print two integers $ p $ and $ c $ — the number of outside walls in an optimal lab, and the remainder of the number of ways by prime modulo $ m $ .
输入输出样例
输入样例 #1
3 1
1
2
7输出样例 #1
1 1
#
1 2
##
2 4
.###
####输入样例 #2
3 2
1000000007
1
2
7输出样例 #2
4 1
6 2
12 22说明
Consider the second example. If $ n=1 $ , the only way to build a lab is to place a single block. In this case, the perimeter will be equal to four. When $ n=2 $ , you must place two blocks side by side. This can be done either vertically or horizontally, so there are two ways. It is easy to see that the lab has six outside walls in this case. For $ n=7 $ , all the $ 22 $ optimal plans are shown in the picture below. 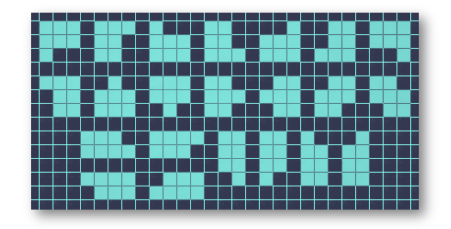Input
题意翻译
在一个无限大的网格图中,选 $n$ 个联通的格子,使这些格子构成的图形周长最小。 若 $u=1$,则构造出一种可行的周长最小的方案。 若 $u=2$,请输出最小的周长及可行的周长最小方案个数对 $m$ 取模的结果,保证 $m$ 为质数。 $n\leq 4\times 10^5$,$T\leq 2\times 10^5$,$10^8\leq m\leq 10^9+9$。Output
题目描述
火星科学家正在积极进行空间研究。其中,冥王星是他们的一个最高优先事项。为了更详细地研究这个星球,决定在冥王星上建立一个实验室。
已知实验室将由n个相等大小的方形积木建成。为了方便起见,我们将假设冥王星的表面是一个由垂直和水平线划分成单位正方形的平面。每个正方形要么被实验室积木占据,要么不被占据,且只有n个正方形被占据。
由于每个积木都是方形的,所以它有四面墙。如果一面墙与另一个积木相邻,则认为它是内部的,否则认为是外部的。
冥王星以其极端寒冷的温度而闻名,因此实验室的外墙必须进行隔热。每面外墙需要一单位隔热材料。因此,实验室外墙的总长度(即其周长)越大,所需的隔热材料就越多。
考虑下面图中的实验室布局。它显示实验室由n = 33个积木组成,所有积木共有24个外墙,即需要24单位隔热材料。
您应该以最优的方式构建实验室,即最小化隔热材料的数量。另一方面,可能有许多最优选择,因此科学家可能对使用最少数量的隔热材料构建实验室的方式的数量感兴趣,模一个素数m。
如果两个方案在无旋转的情况下重叠,则认为它们是相同的。因此,如果实验室计划旋转90°,那么这种新的计划可以被认为是一种单独的方式。
为了帮助科学家探索冥王星,您需要编写一个解决这些难题的程序。
输入输出格式
输入格式
第一行包含两个整数t和u(1≤t≤2∗105,1≤u≤2)——测试用例的数量和测试类型。如果u=1,则需要找到构建实验室的任何最优方式,如果u=2,则需要计算构建实验室的方式的数量。
如果u=2,那么在接下来的输入行中有一个素数m(108≤m≤109+9),需要模m计算方式的数量。
接下来的t行中的每一行都包含一个测试用例的描述,由一个整数n(1≤n≤4∗105)组成——实验室应该由多少积木组成。
保证如果u=1,那么所有测试用例的n之和不超过8∗105。
输出格式
对于每个测试用例,按照下面的格式输出答案,用换行符分隔。输出格式取决于输入数据中的u。
如果u=1,则在第一行中需要打印两个整数h和w——实验室应构建的区域的高度和宽度。然后在接下来的h行中,必须输出一个由w个字符"#"和"。"组成的行si。如果行si的第j个字符是"#",则相应的正方形必须包含实验室的一个积木,否则认为是空的。这样我们就得到了一个符号矩阵。还必须满足矩阵的第一行和最后一行,以及第一列和最后一列至少有一个字符"#",否则我们可以输出相同的实验室布局,但h和w更小。如果有多种构建最优实验室的选择,可以打印其中任何一种。
如果u=2,则需要打印两个整数p和c——最优实验室的外墙数量和方式数量模素数m的余数。
输入输出样例
输入样例 #1
3 1
1
2
7
输出样例 #1
1 1
#
1 2
##
2 4
.###
####
输入样例 #2
3 2
1000000007
1
2
7
输出样例 #2
4 1
6 2
12 22
说明
考虑第二个示例。
如果n=1,构建实验室的唯一方式是放置一个单独的积木。在这种情况下,周长等于四。
当n=2时,您必须将两个积木并排放置。这可以垂直或水平完成,因此有两种方式。很容易看出,在这种情况下实验室有六面外墙。
对于n=7,所有22个最优计划在下面的图片中显示。题目描述 火星科学家正在积极进行空间研究。其中,冥王星是他们的一个最高优先事项。为了更详细地研究这个星球,决定在冥王星上建立一个实验室。 已知实验室将由n个相等大小的方形积木建成。为了方便起见,我们将假设冥王星的表面是一个由垂直和水平线划分成单位正方形的平面。每个正方形要么被实验室积木占据,要么不被占据,且只有n个正方形被占据。 由于每个积木都是方形的,所以它有四面墙。如果一面墙与另一个积木相邻,则认为它是内部的,否则认为是外部的。 冥王星以其极端寒冷的温度而闻名,因此实验室的外墙必须进行隔热。每面外墙需要一单位隔热材料。因此,实验室外墙的总长度(即其周长)越大,所需的隔热材料就越多。 考虑下面图中的实验室布局。它显示实验室由n = 33个积木组成,所有积木共有24个外墙,即需要24单位隔热材料。 您应该以最优的方式构建实验室,即最小化隔热材料的数量。另一方面,可能有许多最优选择,因此科学家可能对使用最少数量的隔热材料构建实验室的方式的数量感兴趣,模一个素数m。 如果两个方案在无旋转的情况下重叠,则认为它们是相同的。因此,如果实验室计划旋转90°,那么这种新的计划可以被认为是一种单独的方式。 为了帮助科学家探索冥王星,您需要编写一个解决这些难题的程序。 输入输出格式 输入格式 第一行包含两个整数t和u(1≤t≤2∗105,1≤u≤2)——测试用例的数量和测试类型。如果u=1,则需要找到构建实验室的任何最优方式,如果u=2,则需要计算构建实验室的方式的数量。 如果u=2,那么在接下来的输入行中有一个素数m(108≤m≤109+9),需要模m计算方式的数量。 接下来的t行中的每一行都包含一个测试用例的描述,由一个整数n(1≤n≤4∗105)组成——实验室应该由多少积木组成。 保证如果u=1,那么所有测试用例的n之和不超过8∗105。 输出格式 对于每个测试用例,按照下面的格式输出答案,用换行符分隔。输出格式取决于输入数据中的u。 如果u=1,则在第一行中需要打印两个整数h和w——实验室应构建的区域的高度和宽度。然后在接下来的h行中,必须输出一个由w个字符"#"和"。"组成的行si。如果行si的第j个字符是"#",则相应的正方形必须包含实验室的一个积木,否则认为是空的。这样我们就得到了一个符号矩阵。还必须满足矩阵的第一行和最后一行,以及第一列和最后一列至少有一个字符"#",否则我们可以输出相同的实验室布局,但h和w更小。如果有多种构建最优实验室的选择,可以打印其中任何一种。 如果u=2,则需要打印两个整数p和c——最优实验室的外墙数量和方式数量模素数m的余数。 输入输出样例 输入样例 #1 3 1 1 2 7 输出样例 #1 1 1 # 1 2 ## 2 4 .### #### 输入样例 #2 3 2 1000000007 1 2 7 输出样例 #2 4 1 6 2 12 22 说明 考虑第二个示例。 如果n=1,构建实验室的唯一方式是放置一个单独的积木。在这种情况下,周长等于四。 当n=2时,您必须将两个积木并排放置。这可以垂直或水平完成,因此有两种方式。很容易看出,在这种情况下实验室有六面外墙。 对于n=7,所有22个最优计划在下面的图片中显示。
火星科学家正在积极进行空间研究。其中,冥王星是他们的一个最高优先事项。为了更详细地研究这个星球,决定在冥王星上建立一个实验室。
已知实验室将由n个相等大小的方形积木建成。为了方便起见,我们将假设冥王星的表面是一个由垂直和水平线划分成单位正方形的平面。每个正方形要么被实验室积木占据,要么不被占据,且只有n个正方形被占据。
由于每个积木都是方形的,所以它有四面墙。如果一面墙与另一个积木相邻,则认为它是内部的,否则认为是外部的。
冥王星以其极端寒冷的温度而闻名,因此实验室的外墙必须进行隔热。每面外墙需要一单位隔热材料。因此,实验室外墙的总长度(即其周长)越大,所需的隔热材料就越多。
考虑下面图中的实验室布局。它显示实验室由n = 33个积木组成,所有积木共有24个外墙,即需要24单位隔热材料。
您应该以最优的方式构建实验室,即最小化隔热材料的数量。另一方面,可能有许多最优选择,因此科学家可能对使用最少数量的隔热材料构建实验室的方式的数量感兴趣,模一个素数m。
如果两个方案在无旋转的情况下重叠,则认为它们是相同的。因此,如果实验室计划旋转90°,那么这种新的计划可以被认为是一种单独的方式。
为了帮助科学家探索冥王星,您需要编写一个解决这些难题的程序。
输入输出格式
输入格式
第一行包含两个整数t和u(1≤t≤2∗105,1≤u≤2)——测试用例的数量和测试类型。如果u=1,则需要找到构建实验室的任何最优方式,如果u=2,则需要计算构建实验室的方式的数量。
如果u=2,那么在接下来的输入行中有一个素数m(108≤m≤109+9),需要模m计算方式的数量。
接下来的t行中的每一行都包含一个测试用例的描述,由一个整数n(1≤n≤4∗105)组成——实验室应该由多少积木组成。
保证如果u=1,那么所有测试用例的n之和不超过8∗105。
输出格式
对于每个测试用例,按照下面的格式输出答案,用换行符分隔。输出格式取决于输入数据中的u。
如果u=1,则在第一行中需要打印两个整数h和w——实验室应构建的区域的高度和宽度。然后在接下来的h行中,必须输出一个由w个字符"#"和"。"组成的行si。如果行si的第j个字符是"#",则相应的正方形必须包含实验室的一个积木,否则认为是空的。这样我们就得到了一个符号矩阵。还必须满足矩阵的第一行和最后一行,以及第一列和最后一列至少有一个字符"#",否则我们可以输出相同的实验室布局,但h和w更小。如果有多种构建最优实验室的选择,可以打印其中任何一种。
如果u=2,则需要打印两个整数p和c——最优实验室的外墙数量和方式数量模素数m的余数。
输入输出样例
输入样例 #1
3 1
1
2
7
输出样例 #1
1 1
#
1 2
##
2 4
.###
####
输入样例 #2
3 2
1000000007
1
2
7
输出样例 #2
4 1
6 2
12 22
说明
考虑第二个示例。
如果n=1,构建实验室的唯一方式是放置一个单独的积木。在这种情况下,周长等于四。
当n=2时,您必须将两个积木并排放置。这可以垂直或水平完成,因此有两种方式。很容易看出,在这种情况下实验室有六面外墙。
对于n=7,所有22个最优计划在下面的图片中显示。题目描述 火星科学家正在积极进行空间研究。其中,冥王星是他们的一个最高优先事项。为了更详细地研究这个星球,决定在冥王星上建立一个实验室。 已知实验室将由n个相等大小的方形积木建成。为了方便起见,我们将假设冥王星的表面是一个由垂直和水平线划分成单位正方形的平面。每个正方形要么被实验室积木占据,要么不被占据,且只有n个正方形被占据。 由于每个积木都是方形的,所以它有四面墙。如果一面墙与另一个积木相邻,则认为它是内部的,否则认为是外部的。 冥王星以其极端寒冷的温度而闻名,因此实验室的外墙必须进行隔热。每面外墙需要一单位隔热材料。因此,实验室外墙的总长度(即其周长)越大,所需的隔热材料就越多。 考虑下面图中的实验室布局。它显示实验室由n = 33个积木组成,所有积木共有24个外墙,即需要24单位隔热材料。 您应该以最优的方式构建实验室,即最小化隔热材料的数量。另一方面,可能有许多最优选择,因此科学家可能对使用最少数量的隔热材料构建实验室的方式的数量感兴趣,模一个素数m。 如果两个方案在无旋转的情况下重叠,则认为它们是相同的。因此,如果实验室计划旋转90°,那么这种新的计划可以被认为是一种单独的方式。 为了帮助科学家探索冥王星,您需要编写一个解决这些难题的程序。 输入输出格式 输入格式 第一行包含两个整数t和u(1≤t≤2∗105,1≤u≤2)——测试用例的数量和测试类型。如果u=1,则需要找到构建实验室的任何最优方式,如果u=2,则需要计算构建实验室的方式的数量。 如果u=2,那么在接下来的输入行中有一个素数m(108≤m≤109+9),需要模m计算方式的数量。 接下来的t行中的每一行都包含一个测试用例的描述,由一个整数n(1≤n≤4∗105)组成——实验室应该由多少积木组成。 保证如果u=1,那么所有测试用例的n之和不超过8∗105。 输出格式 对于每个测试用例,按照下面的格式输出答案,用换行符分隔。输出格式取决于输入数据中的u。 如果u=1,则在第一行中需要打印两个整数h和w——实验室应构建的区域的高度和宽度。然后在接下来的h行中,必须输出一个由w个字符"#"和"。"组成的行si。如果行si的第j个字符是"#",则相应的正方形必须包含实验室的一个积木,否则认为是空的。这样我们就得到了一个符号矩阵。还必须满足矩阵的第一行和最后一行,以及第一列和最后一列至少有一个字符"#",否则我们可以输出相同的实验室布局,但h和w更小。如果有多种构建最优实验室的选择,可以打印其中任何一种。 如果u=2,则需要打印两个整数p和c——最优实验室的外墙数量和方式数量模素数m的余数。 输入输出样例 输入样例 #1 3 1 1 2 7 输出样例 #1 1 1 # 1 2 ## 2 4 .### #### 输入样例 #2 3 2 1000000007 1 2 7 输出样例 #2 4 1 6 2 12 22 说明 考虑第二个示例。 如果n=1,构建实验室的唯一方式是放置一个单独的积木。在这种情况下,周长等于四。 当n=2时,您必须将两个积木并排放置。这可以垂直或水平完成,因此有两种方式。很容易看出,在这种情况下实验室有六面外墙。 对于n=7,所有22个最优计划在下面的图片中显示。