300191: CF39G. Inverse Function
Memory Limit:64 MB
Time Limit:5 S
Judge Style:Text Compare
Creator:
Submit:0
Solved:0
Description
Inverse Function
题意翻译
### 题目描述 Petya写了一个C++程序以计算一个很有意思的函数 $f(n)$。她给了一个输入值给这个程序,就跑去厨房喝茶了。当Petya回来时,程序已经计算出了结果。 然而她去喝茶时,一个狡猾的病毒把输入文件摧毁了!Petya现在没法知道她给了 $f(n)$ 什么值。所以,这个任务就交给你了! Petya给你的程序由以下简化了的C++语法构成: * 函数声明($\text{function}$):```int f(int n){operatorSequence}```; * 语句序列($\text{operatorSequence}$):```operator```|```operator operatorSequence```(也就是说,$\text{operatorSequence}$可能是一个操作符,也可能在一个操作符后面还有其他的语句); * 操作符($\text{operator}$):```return arithmExpr```|```if(logicalExpr)return arithmExpr```; * 逻辑表达式($\text{logicalExpr}$):```arithmExpr``` ```<```|```>```|```==``` ```arithmExpr```(即对两个数学表达式比较值的大小); * 数学表达式($\text{arithmExpr}$):```sum```; * 求值结果($\text{sum}$):```product```|```sum+product```|```sum-product```; * 乘积($\text{product}$):```multiplier```|```product*multiplier```|```product/multiplier```; * 因数($\text{multiplier}$): ```n```|```number```|```f(arithmExpr)```(对这是一个递归函数。那个```n```就是你给这层调用传的参) * 数字($\text{number}$): $n,n\in[0,2^{15})\cup\N$。(即 $0$ 至 $32767$ 间的任何整数。) $\text{operatorSequence}$ 中的空白是可自定义的,只要能分开两个不同的东西即可。(和原来的C++一样。) 关于这些 $\text{operator}$(其实就只有```return```和```if```)的用途,和原来的C++一样,我就不再赘述。保证不会出现C++里其他的东西——循环、赋值语句、嵌套表达式,等等。函数声明中,除了参数变量```n```,不会有任何其他的变量。所有整数常量都在 $[0,2^{15})$ 间。 语句是有顺序地执行的。```return```语句被执行后,后面的语句不再执行。所有东西的优先级和标准C++一样。也就是说,先乘除后加减,等等。关系运算符含义与标准C++没有什么两样。 **现在请注意!这个程序使用** $\textbf{15-bit}$ **Berland C++编译器编译。也就是说,所有中间值请模** $\textbf{32768}$。(对于负数,想一想你做P1082时是怎么处理的。)**除法无论何时,都是整数除法,即余数会被忽略。** 一些例子: $12345+23456=3033,0-1=32767,1024\times1024=0,1000/3=333$。 当然,无论这个函数的参数是多少,这个函数总能成功执行。也就是说: * 永远不可能除以 $0$。 * 当这个函数被递归调用时,下一层的参数总小于这一层的参数。在这种情况下,函数不可能无限递归。 * 函数总会返回一个值。 还有,值得一提,$f(n)$ 的返回值只依赖于参数。这就是为什么 $f(n)$ 可以被视为数学意义上的函数—— >一般地,在一个变化过程中,如果有两个变量 $x$ 和 $y$,并且对于 $x$ 的每一个值,$y$ 都有一个唯一确定的值与其对应,那么我们就说 $x$ 是自变量(independent variable),$y$ 是 $x$ 的函数(function)。——八年级下册数学书 ~~没错真正的题目只有一行,前面都是铺垫:~~ 给定 $f(n)$,请求出 $n$。如果有多种可能,请选择最大的一种作为答案。 ### 输入格式 第一行一个整数 $f(n)$。 从第二行开始,是对 $f$ 函数的定义。 输入文件大小不超过 $100~\text{Bytes}$。 ### 输出格式 一行一个整数,为你求出的 $n$。如果无解,输出 $-1$。题目描述
Petya wrote a programme on C++ that calculated a very interesting function $ f(n) $ . Petya ran the program with a certain value of $ n $ and went to the kitchen to have some tea. The history has no records concerning how long the program had been working. By the time Petya returned, it had completed the calculations and had the result. However while Petya was drinking tea, a sly virus managed to destroy the input file so that Petya can't figure out for which value of $ n $ the program was run. Help Petya, carry out the inverse function! Mostly, the program consists of a function in C++ with the following simplified syntax: - $ function $ ::= int f(int n) { $ operatorSequence $ } - $ operatorSequence $ ::= $ operator | operator operatorSequence $ - $ operator $ ::= return $ arithmExpr $ ; $ | $ if ( $ logicalExpr $ ) return $ arithmExpr $ ; - $ logicalExpr $ ::= $ arithmExpr>arithmExpr $ $ | $ $ arithmExpr<arithmExpr $ $ | $ $ arithmExpr $ == $ arithmExpr $ - $ arithmExpr $ ::= $ sum $ - $ sum $ ::= $ product $ $ | $ $ sum+product $ $ | $ $ sum-product $ - $ product $ ::= $ multiplier $ $ | $ $ product*multiplier $ $ | $ $ product/multiplier $ - $ multiplier $ ::= n $ | $ $ number $ $ | $ f( $ arithmExpr $ ) - $ number $ ::= $ 0|1|2|...\ |32767 $ The whitespaces in a $ operatorSequence $ are optional. Thus, we have a function, in which body there are two kinds of operators. There is the operator "return $ arithmExpr $ ;" that returns the value of the expression as the value of the function, and there is the conditional operator "if ( $ logicalExpr $ ) return $ arithmExpr $ ;" that returns the value of the arithmetical expression when and only when the logical expression is true. Guaranteed that no other constructions of C++ language — cycles, assignment operators, nested conditional operators etc, and other variables except the $ n $ parameter are used in the function. All the constants are integers in the interval $ [0..32767] $ . The operators are performed sequentially. After the function has returned a value other operators in the sequence are not performed. Arithmetical expressions are performed taking into consideration the standard priority of the operations. It means that first all the products that are part of the sum are calculated. During the calculation of the products the operations of multiplying and division are performed from the left to the right. Then the summands are summed, and the addition and the subtraction are also performed from the left to the right. Operations ">" (more), "<" (less) and "==" (equals) also have standard meanings. Now you've got to pay close attention! The program is compiled with the help of $ 15 $ -bit Berland C++ compiler invented by a Berland company BerSoft, that's why arithmetical operations are performed in a non-standard way. Addition, subtraction and multiplication are performed modulo $ 32768 $ (if the result of subtraction is negative, then $ 32768 $ is added to it until the number belongs to the interval $ [0..32767] $ ). Division "/" is a usual integer division where the remainder is omitted. Examples of arithmetical operations: 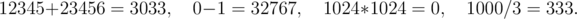Guaranteed that for all values of $ n $ from $ 0 $ to $ 32767 $ the given function is performed correctly. That means that: 1\. Division by $ 0 $ never occures. 2\. When performing a function for the value $ n=N $ recursive calls of the function $ f $ may occur only for the parameter value of $ 0,1,...,N-1 $ . Consequently, the program never has an infinite recursion. 3\. As the result of the sequence of the operators, the function always returns a value. We have to mention that due to all the limitations the value returned by the function $ f $ is independent from either global variables or the order of performing the calculations of arithmetical expressions as part of the logical one, or from anything else except the value of $ n $ parameter. That's why the $ f $ function can be regarded as a function in its mathematical sense, i.e. as a unique correspondence between any value of $ n $ from the interval $ [0..32767] $ and a value of $ f(n) $ from the same interval. Given the value of $ f(n) $ , and you should find $ n $ . If the suitable $ n $ value is not unique, you should find the maximal one (from the interval $ [0..32767] $ ).输入输出格式
输入格式
The first line has an integer $ f(n) $ from the interval $ [0..32767] $ . The next lines have the description of the function $ f $ . In the description can be found extra spaces and line breaks (see the examples) which, of course, can’t break key words int, if, return and numbers. The size of input data can’t exceed $ 100 $ bytes.
输出格式
Output a single number — the answer to the problem. If there’s no answer, output "-1" (without quotes).
输入输出样例
输入样例 #1
17
int f(int n)
{
if (n < 100) return 17;
if (n > 99) return 27;
}
输出样例 #1
99
输入样例 #2
13
int f(int n)
{
if (n == 0) return 0;
return f(n - 1) + 1;
}
输出样例 #2
13输入样例 #3
144
int f(int n)
{
if (n == 0) return 0;
if (n == 1) return n;
return f(n - 1) + f(n - 2);
}输出样例 #3
24588